
Barley gene family homologous to maize rust resistance gene Rp1-D
N. Rostoks1, J.M. Zale2, J. Soule2, R. Brueggeman1, A. Druka1,
D. Kudrna1, and A. Kleinhofs1
1 Department of Crop and Soil Sciences, Washington State University,
Pullman, WA 99164-6420, USA
2 Present address: USDA Wheat Genetics, Quality, Physiology, and Disease Research
Unit, 209 Johnson Hall, Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164-6420, USA
Abstract
Reported plant disease resistance genes encode proteins, which have conserved motifs in
nucleotide binding site (NBS). Conservation extends across different species, therefore
resistance genes from one species can be used to isolate homologous regions from
another employing DNA sequences encoding conserved protein motifs as probes. Despite
similarity in sequence, function of such homologues is often unknown, hence they are
usually referred to as resistance gene analogs (RGAs).
Here we report isolation and characterization of barley RGA family homologous
to the maize rust resistance gene Rp1-D. Family members were isolated using the maize
pic20 probe (Collins et al., 1998; received from Dr. A. Pryor), which is 98% homologous
to maize Rp1-D gene NBS region. Pic20 probe was of particular interest to us, because it
was reported to co-segregate with a barley stem rust resistance gene Rpg1 (Ayliffe et al.,
2000). Our results indicate that, although structurally similar to plant disease resistance
genes, barley pic20 homologues co-segregate neither with Rpg1, nor with any other
known disease resistance gene in barley.
Mapping and subcloning of barley pic20 homologues
Pic20 probe hybridized to 10 cv. Morex genomic DNA HindIII bands designated A to I
and was used to screen a 6.3x barley cv. Morex BAC library. 60 BAC clones were
selected and Southern analysis of their HindIII restriction digests with pic20 probe
confirmed that all bands are present. Representatives of all bands were subcloned and
mapped on Steptoe x. Morex RFLP Bin map
(http://barleygenomics.wsu.edu/databases/databases.html). G band represents two
different HindIII fragments of the same size. H and I bands represent a contiguous DNA
fragment cleaved by a HindIII restriction site. Map locations of barley pic20 homologues
are listed in Table 1.
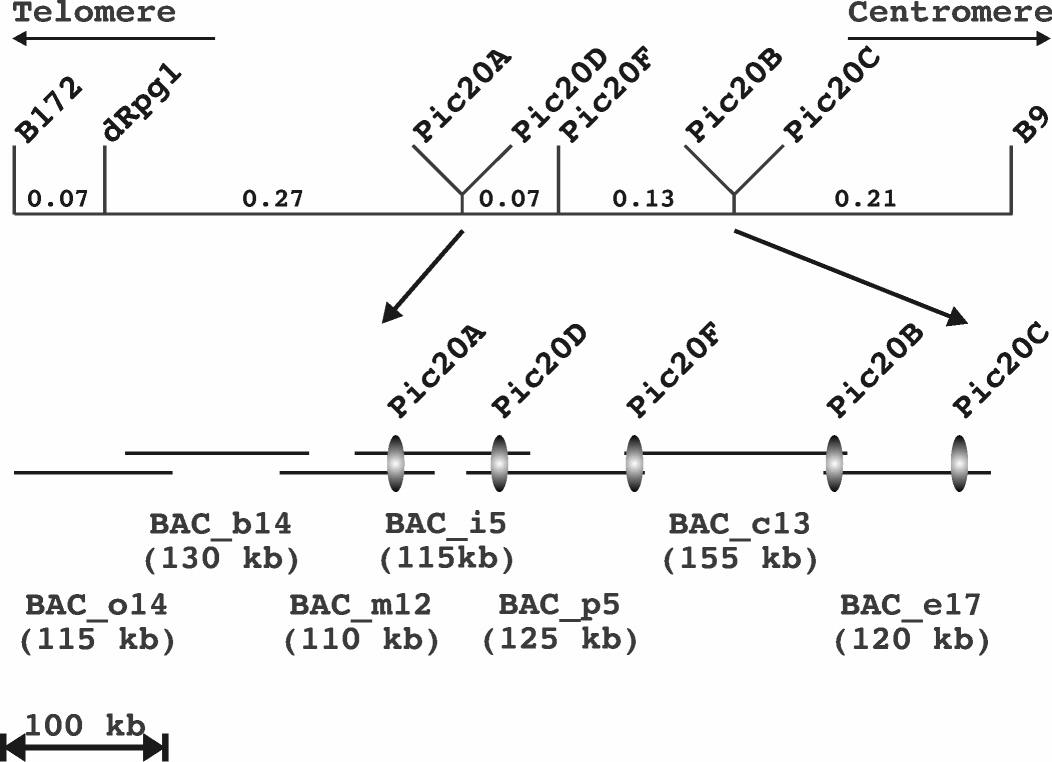
A recombinant genetic map of Pic20A, B, C, D and F bands and Rpg1 region, as
well as corresponding BAC contig is shown in Figure 1. Genetic distances are based on
recombinant mapping of 3000 gametes. Pic20A locus, which is the closest to Rpg1 and
has been reported to co-segregate with it (Ayliffe et al., 2000; pic20c1 locus from M1-13
clone), is 0.27 cM away from Rpg1 gene in our experiments.
Barley BAC clone contig encompassing Pic20A, B, C, D and F bands spans
approximately 700 kb and extends ca. 200 kb from Pic20A towards Rpg1.
Sequence analysis of barley pic20 homologues
Representative of every band was sequenced in the pic20 homology region. All but one
(C band) represent contiguous open reading frame in the pic20 homology part, although
some of them have non-sense mutations and retrotransposon insertions upstream or
downstream. DNA and deduced amino acid sequences of barley pic20 homologues were
aligned with pic20 sequence. High degree of homology was observed among all
sequences ranging from 50 - 87% identity at DNA level and from 60 - 84% identity at
amino acid level.
cDNA library screening
We screened several arrayed barley EST libraries representing 200,000 clones (Close et
al., 2001)) with maize pic20 probe and several barley pic20 homologues. Positive clones
were not identified suggesting low expression levels of barley pic20 homologues.
However, 2 different cDNAs were PCR-amplified from the bulk cDNA libraries. Both
were identical to previously identified barley pic20 genomic clones. cDNA
corresponding to A band was amplified from cv. Morex embryo cDNA library, whereas
cDNA corresponding to C band was amplified from cv. Morex seedling green leaf cDNA
library. The presence of cDNA corresponding to C band is somewhat surprising, since C
band has a non-sense mutation in NBS region. It suggests a rather recent mutation event,
since no other mutations have accumulated after removal of selective pressure.
Summary
Barley pic20 homologues represent a family of genes and pseudogenes homologous to
NBS-LRR plant disease resistance genes, but not co-segregating genetically with any
known barley resistance gene. Although presently their function remains unknown,
structure conservation suggests their involvement in barley resistance responses and
probably in evolution of disease resistance genes.
Table 1. Location of barley pic20 homologues on Steptoe x Morex RFLP Bin map.
|
Chromosome |
Bin |
Flanking Bin
Markers |
| Pic20A |
1(7H) |
1 |
ABG704 - ABG320 |
| Pic20B |
1(7H) |
1 |
ABG704 - ABG320 |
| Pic20C |
1(7H) |
1 |
ABG704 - ABG320 |
| Pic20D |
1(7H) |
1 |
ABG704 - ABG320 |
| Pic20E |
3(3H) |
8 |
ABG377 - ABG453 |
| Pic20F |
1(7H) |
1 |
ABG704 - ABG320 |
| Pic20G1 |
7(5H) |
14 |
ABG390 - ABG463 |
| Pic20G2 |
6(6H) |
5 |
ABG387B - Ldh1 |
| Pic20H,I |
5(1H) |
13 |
BCD1930 - ABC261 |
Figure 1. Genetic map of barley Rpg1 and Pic20A, B, C, D and F region (top) and BAC
clone contig of Pic20A, B, C, D and F region (bottom). Genetic distances are based on
recombinant mapping in 3000 gamete population.
References
Ayliffe, M.A., Collins, N.C., Ellis, J.G. and Pryor, A. (2000). The maize rp1 rust
resistance gene identifies homologues in barley that have been subjected to
diversifying selection. Theor Appl Genet 100, 1144-1154.
Collins, N.C., Webb, C.A., Seah, S., Ellis, J.G., Hulbert, S.H. and Pryor, A. (1998). The
isolation and mapping of disease resistance gene analogs in maize. MPMI 11,
968-978.
Close, T.J., Wing, R., Kleinhofs, A. and Wise, R.P. (2001). Genetically and physically
anchored EST resources for barley genomics. Plant and Animal Genome IX
Conference W28, San Diego, USA.

