The brachytic class of semidwarf mutants in barley
J.D. Franckowiak
Department of Plant Sciences, North Dakota State University,
Fargo, ND 58105, U.S.A.
The collection of plant height or semidwarf mutants in barley contains several
phenotypic groups or classes of mutants (Franckowiak and Pecio, 1992). The
mutants in one of the more distinctive classes are those which have a brachytic
phenotype. The coleoptile and the first foliage leaf are shorter than normal
and the seedlings fail to respond to the application of gibberellin (Boulger et
al., 1982). The leaf blades, culms, spikes, awns, and kernels of brachytic
mutants may be shorter than in normal sister lines. Alleles at two loci, the
br1 (ari-i) locus in chromosome 1S (Powers, 1936) and the
br2 locus in chromosome 4S (Tsuchiya, 1980), have been reported to
control expression of the brachytic phenotype in barley. But, other mutants
have a similar phenotype (Tsuchiya, 1974; 1976) and some lines without these
genes are insensitive to gibberellic acid treatment (Boulger et al., 1982;
Franckowiak and Pecio, 1992).
Bowman backcross derived lines from entries in the barley semidwarf
collection, which exhibited several brachytic traits (Franckowiak and Pecio,
1992), were plant in the 1994 spring greenhouse nursery (Table 1). These lines
were used because the original stocks included both spring and winter barley
cultivars and showed variable responses to photoperiod. Nearly all of the
selected lines had a short blade on the first true leaf. Reduced plant height,
coiled neck, long basal rachis internode, short awn, and short kernel were
observed in some, but not all lines.
Lines having similar phenotypes were noted and few crosses were made to
determine allelism. The F1 progenies in which the plants exhibited brachytic
characteristics and provided evidence for allelism are listed in Table 2. The
results show that DWS1038, DWS1224, and FN53 each have a mutant gene at the
br1 locus. The ari-l.3 gene is the mutant in the breviaristatum
series of loci which is allelic at the br2 locus. The DWS1002 and
DWS1230 stocks contain brachytic mutants which are alleles. The mutants in
the DWS1036 and DWS1037 stocks are alleles. Allelism between these two groups
was not tested. However, neither is allelic at the br1 locus (Table 2).
The crosses, which are needed to demonstrate that these mutants represent new
loci, have not been made.
References
Boulger, M.C., R.G. Sears, and W.E. Kronstad. 1982. An investigation of the
association between dwarfing sources and gibberellic acid response in barley.
Barley Genet. IV:550-553.
Franckowiak, J.D., and A. Pecio. 1992. Coordinator's report: Semidwarf genes: A
listing of genetic stocks. BGN 21:116-127.
Table 1. A list of mutants from the barley semidwarf collection placed
in the brachytic phenotypic class.

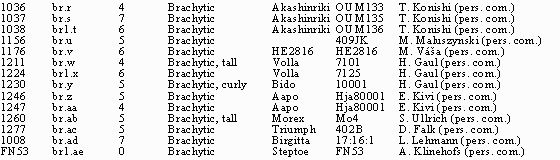
ıAllele symbols recommended for mutants in the brachytic class of
semidwarf genes. A period is use to separate the locus and allele portions of
the gene symdol. If the br symbol is followed by a number, the mutant
gene is assigned to a specific locus. If it is not, adequate allelism testing
has not been completed to assign the mutant gene to a specific locus.
Powers, L. 1936. The nature of the interactions of genes affecting four
quantitative characters in a cross between Hordeum deficiens and
vulgare. Genetics 21:398-420.
Stoy, V., and A. Hagberg. 1967. Effects of growth regulators on ear density
mutants in barley. Hereditas 58:359-384.
Tsuchiya, T. 1980. BGS157. Brachytic 2, br2 (revised). BGN 10:115.
Tsuchiya, T. 1974. Allelic relationships of genes for short-awned mutants in
barley. BGN 4:80-81
Tsuchiya, T. 1976. Allelism testing of genes between brachytic and erectoides
mutants. BGN 6:79-81.
Table 2. Crosses among selected lines to determine allelism among
mutant genes which control the brachytic growth habit.
_________________________________________________________
Female Male Allele symbolsı No. of Phenotype
parent parent ________________ plants of F1 plants
Male Female
_________________________________________________________
DWS1078 FN53 br1.a br1.ae 15 Brachytic
DWS1132 DWS1038 ari-i.38² br1.t 11 Brachytic
DWS1132 DWS1224 ari-i.38 br1.x 15 Brachytic
DWS1136 DWS1152 ari-m.28 br1.e 9 Normal
DWS1079 DWS1136 br2.b ari-m.28 9 Normal
DWS1135 DWS1079 ari-l.3 br2.b 18 Brachytic
DWS1002 DWS1132 br.g ari-i.38 9 Normal
DWS1002 DWS1230 br.g br.y 15 Brachytic
DWS1036 DWS1037 br.r br.s 8 Brachytic
DWS1036 DWS1152 br.r br1.e 9 Normal
__________________________________________________________
ıThe recommended allele symbols are listed in Table 1 and are
modified to indicate the results of the crosses considered in this report.
²Positive allelism tests for the ari-i.38 and
br1.e mutants at the br1 locus were eported by Tsuchiya (1974)
and Szarejko and Maluszynski (1984), respectively.

