
Figure 1. OP-Z04 RAPD pattern of bulks, DH-lines and cultivars susceptable (s) and resistant (r,ym4) to BaMMV
Linkage analysis was carried out on 287 F/1/ anther derived doubled haploid (DH) barley lines out of a cross between the BaMMV/BaYMV susceptible barley cultivar 'Igri' and the resistant cultivar 'Franka'. Five plants of each DH-line were tested for resistance to BaMMV in two replications using mechanical inoculation according to Friedt (1983). BaMMV-reaction was estimated by DAS-ELISA using antiserum kindly provided by Dr. W. Huth, Federal Biological Research Center, Braunschweig, Germany. In order to test a large number of random primers for polymorphism and linkage in a short periode of time, "bulked segregant analysis" according to Michelmore et al. (1991) was carried out with bulks containing DNA of 15 DH-lines each. DNA extraction was performed according to Graner et al. (1991). PCR reaction mixtures (25µl) contained 25ng genomic DNA, 0.4 mM dNTPs, 6mM MgCl/2/, 0.3 uM of a random 10mer primer (Operon Technologies Inc.) and 1.5 U AmpliTaq DNA-polymerase Stoffel fragment (Perkin Elmer) with the corresponding Stoffel reaction buffer (Perkin Elmer). The mixture was overlaid with mineral oil and amplification was carried out in a Perkin Elmer DNA thermocycler 480 using the following temperature profile: an initial denaturation step (94°C/4min) was followed by 45 cycles of 94°C/1min, 36°C/1min, 72°C/2min. Heating rate was restricted to 5°C/min from 36°C to 72°C (modified after Sobral & Honeycutt 1993) and the polymerization step was extended for 4s/cycle at 72°C. Fragments were separated on a 2% agarose gel [sea plaque agarose (FMC) : standard agarose (FMC) = 1 : 1] with 3V/cm, stained in ethidium bromide and visiualized on an UV-screen (286nm). Linkage analysis was conducted using Mapmaker computer software (Lander et al. 1987) and crossover units were converted into map distances (centiMorgans, cM) by applying the Kosambi function (Kosambi 1944).
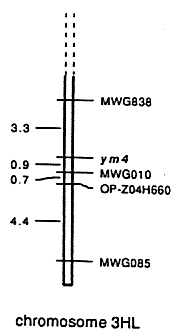
A total of 148 decamer primers was screened to identify polymorphisms between the resistant and the susceptible bulk. Only primer OP-Z04 (5'-AGGCTGTGCT-3') revealed polymorphism resulting in an additional 660bp-band in the susceptible bulk, whereas other bands generated by this primer were identical (Figure 1). In order to investigate whether this polymorphism is linked to the ym4 resistance gene, DH-lines as well as their parents were analysed. While the 660bp-band was present in the susceptible cultivar 'Igri' it was missing in the resistant cv. 'Franka'. The same was true for susceptible and resistant DH-lines derived from the cross between these two cultivars (Figure 1). By testing 287 DH-lines a cosegregation of OP-Z04H660 with the RFLP-marker MWG10, which is very closely linked to ym4, was observed (Figure 2). In the map the distance between MWG010 and OP-Z04H660 was calculated to be 0.7 cM by Mapmaker. This may be due to the fact that not all DH-lines included in RFLP mapping were tested in the RAPD-analysis, yet. No recombination between MWG010 and OP-Z04H660 in any of the DH-lines tested up to now was observed. In further experiments susceptible and resistant cultivars released in Germany as well as the possible donor of ym4, i.e., the variety 'Ragusa', were analysed for the presence or absence of OP-Z04H660, respectively. In each case OP-Z04H660 was able to discriminate perfectly between resistant and susceptible cultivars as the additional 660bp-band was present in all susceptible cultivars but missing in all resistant varieties (Table 1).

Figure 1. OP-Z04 RAPD pattern of bulks, DH-lines and cultivars susceptable (s) and resistant (r,ym4) to BaMMV
The results elucidate that OP-Z04H660 is well suited to faciliate marker assisted selection for BaMMV-resistance encoded by ym4. As resistance genes against barley yellow mosaic disease different from ym4 and different from each other are present within the barley gene pool (Götz & Friedt 1993, Ordon & Friedt 1993) future work will concentrate on defining RAPD markers for these resistance genes.
Table 1: Usefulness of OP-Z04H660 in different genetic backgrounds to detect the presence or absence of ym4
______________________________________________________ Resistant cvs. OP-Z04H660 Susceptible cvs. OP-Z04H660 ______________________________________________________ Ragusa - Igri + Franka - Magie + Brunhild - Alraune + Jana - Gerbel + Sonate - Corona + Romanze - Baretta + Express - Catinka + Labea - Danilo + Columbo - Hanna + Venus - Asorbia - Gauloise - Labra - Noveta - Nixe - ______________________________________________________- = absence of OP-Z04H660 linked to resistance, + presence of OP-Z04H660 linked to susceptibility
References:
Friedt, W. 1983. Mechanical transmission of soil-borne barley yellow mosaic virus. Phytopath. Z. 106: 16-22.
Götz, R., and W. Friedt. 1993. Resistance to the barley yellow mosaic virus complex - Differential genotypic reactions and genetics of BaMMV-resistance in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Plant Breeding 111: 125-131.
Graner, A., and E. Bauer. 1993. RFLP mapping of the ym4 virus resistance gene in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 689-693.
Graner, A., A. Jahoor, J. Schondelmaier, H. Siedler, K. Pillen, G. Fischbeck, G. Wenzel, and R. G. Herrmann. 1991. Construction of an RFLP map in barley Theor. Appl. Genet. 83: 250-256.
Huth, W. 1990. The yellow mosaic inducing viruses of barley in Germany. Proc., 1st Symp.Intern.Working Group Plant Viruses with Fungal Vectors, Braunschweig, Germany, August 21-24. 1990, 113-115.
Huth, W., and M. J. Adams. 1990. Barley yellow mosaic virus (BaYMV) and BaYMV-M: two different viruses. Intervirology 31: 38-42.
Kaiser, R., and W. Friedt. 1989. Chromosomal location of resistance to barley yellow mosaic virus in German winter-barley identified by trisomic analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 77: 241-245.
Kaiser, R., and W. Friedt. 1992. Gene for resistance to barley mild mosaic virus in German winter-barley located on chromosome 3L. Plant Breeding 108: 169-172
Kosambi, D. D. 1944. The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12: 172-175.
Lander, E. S., P. Green, J. Abrahamson, A. Barlow. M. J. Daly, S. E. Lincoln, and L. Newburg. 1987. MAPMAKER: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1: 174-181.
Le Gouis, J., F. Ordon, and W. Friedt. 1994. Isozyme-electrophoresis for chromosomal localization of barley mild mosaic virus resistance genes different from ym4. Barley Genet. Newslet. 23: 36-39.
Michelmore, R. W., I. Paran, and R. V. Kesseli. 1991. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance by bulked segregant analysis: A rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 9828-9832.
Ordon F., and W. Friedt. 1993. Mode of inheritance and genetic diversity of BaMMV resistance of exotic barley germplasms carrying genes different from 'ym4'. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 229-233.
Sobral, B. W. S., and R. J. Honeycutt. 1993. High output genetic mapping of polyploids using PCR-generated markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 105-112.