

Genotypes carrying resistance genes against barley mild mosaic virus (BaMMV) different from ym4 which is presumed to be present in all resistant European cultivars and is located on the long arm of chromosome 3 (Kaiser & Friedt, 1989, 1992; Graner & Bauer, 1993) were identified by F2-segregation analysis (Götz & Friedt, 1993). However, nothing is known about the chromosomal localization of these genes. Many isozyme loci have been identified in barley (Brown, 1983; Nielsen & Johansen, 1986) which represent relatively simple and cheap markers provided that their chromosomal localization is known and polymorphism is present. Therefore, corresponding genotypes were checked for polymorphism and F2-progeny of crosses to susceptible cultivars were analyzed for linkage between resistance genes and isozymes in order to assess the possibility offered by isozymes to locate resistance genes against BaMMV different from ym4.
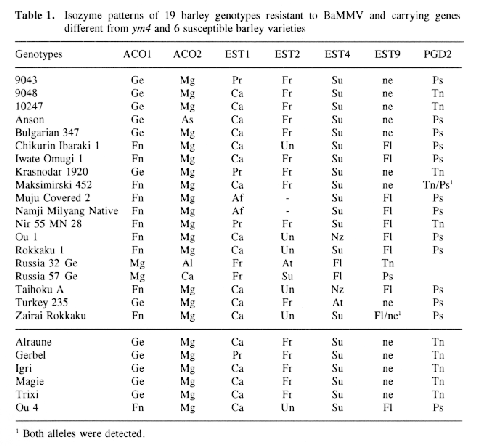
A total of 19 genotypes (pure lines) carrying resistance genes against BaMMV different from ym4 (Götz & Friedt, 1993), and F2 progenies derived from crosses between these genotypes, and six susceptible varieties, i.e., 'Alraune', 'Gerbel' 'Igri', 'Magie', 'Trixi', 'Ou 4', were analyzed for isoenzymatic patterns. The designation of the loci and the alleles followed Nielsen & Johansen (1986) and Hvid & Nielsen (1977). The additional allele As (reference variety 'Anson', C115733) was present for AC02. F2-plants were tested for BaMMV-reaction by mechanical spray-gun inoculation in the greenhouse (cf. Friedt, 1983; Kaiser & Friedt, 1989), and BaMMV-reaction was estimated by DAS-ELISA according to Clark & Adams (1977) using antiserum kindly provided by Dr. W. Huth, Federal Biological Research Center, Braunschweig, Germany. A chi-square test (Chi2) was used to test for agreement between observed and expected segregations for the isozyme and resistance loci, and to test the independance between two loci., respectively. The expected numbers of susceptible and resistant plants used to calculate Chi2 were modified to take into account the rate of infection (J. Jensen, pers. comm.). Recombination rates were estimated according to formulae provided by Wagner et al. (1992).
Out of the 15 isozyme systems tested 12 were monomorphic (GPD, GPI, IDH, MDH, PGM, AAT, ADHI, AMP, CAT, ENP, NDH, GDH) and 3 were polyi-norphic (ACO, EST, PGD). Thus seven polymorphic loci corresponding to the aconitase hydratase (ACO1 and AC02), the esterases (EST1, EST2, EST4 and EST9) and the phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (PGD2) were detected on a total of 26 loci tested providing markers on 4 of the 7 chromosomes. The susceptible cultivars of European origin ('Alraune', 'Gerbel', 'Igri', 'Magie' and 'Trixi') showed a close relationship as far as their isozyme patterns are concerned; only 'Gerbel' differed from the others for ESTI (Table 1).
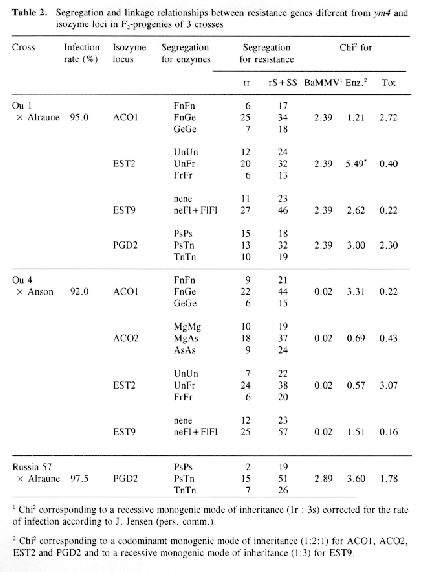
Linkage relationships between isozyme loci and resistance genes different from ym4 were studied in 3 crosses (Table 2). Except for EST2 in the cross 'Ou1' x 'Alraune', the observed segregation for the isozymes fitted well to the expected segregation corresponding to their known mode of inheritance. In all crosses the segregation for resistance fitted to the expected ratio of Ir : 3s for a recessive monogenic mode of inheritance (cf. Ordon & Friedt, 1993). No linkage was found between the resistance gene of 'Ou1 and the isozyme loci ACO1, EST2, EST9, PGD2, between the resistance gene of 'Anson' and the isozyme loci ACO1, AC02, EST2, EST9 and between the resistance gene of 'Russia 57' and the isozyme locus PGD2 (Table 2).
The gene ym4 seems to be allelic to a gene of 'Mokusekko 3' linked to EST1-EST2-EST4 (Konishi et. al., 1989). since F.-progeny of crosses between 'Mokusekko 3 'and resistant German varieties do not segregate susceptible plants (Götz & Friedt, 1993). Therefore, linkage between ym4 and the Est1-Est2-Est4 locus was investigated on 202 F2-plants of the cross 'Ea 52' × 'Ogra'. In these studies a recombination rate of 8.32±2.01 between ym4 and the esterases was estimated, which is similar to the rates reported by Konishi et al. (1989) and Kawada (1991) for the same esterase loci and one of the BaYMV resistance genes of 'Mokusekko 3' (from 0.54 to 6.18%). This result therefore supports the assumption that ym4 is allelic or tightly linked to this gene of 'Mokusekko 3'.
Although previous studies (Brown, 1983; Nielsen & Johansen, 1986) described different alleles for the majority of the isozyme systems tested here, isozyme polymorphism in our sample of genotypes was very low. Even within crosses between genotypes of different origin, i.e., German susceptible varieties and mainly East Asian resistant germplasms. The use of isozymes as markers for resistance genes is obviously rather limited, therefore. The tight linkage between the esterase loci and ym4 seems to be an exception. Consequently, other more powerful tools, like RFLP- or RAPD-techniques, have to be used to locate BaMMV resistance genes.
References:
Brown, A.H.D. 1983. Barley. In: TANKSLEY S. D. and ORTON T. J. [Eds.], Isozymes in plant genetics and breeding, part A, 57-77.
Clark, AX, and M.J. Adams. 1977. Characteristics of the microplate method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of plant viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 34: 475-483.
Friedt, W. 1983. Mechanical transmission of soil-borne barley yellow mosaic virus. Phytopathol. Z. 106: 16-22.
Götz, R., and W. Friedt. 1993. Resistance to the barley yellow mosaic virus complex - Differential genotypic reactions and genetics of BaMMV-resistance of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Plant Breed. 111: 125-13 1.
Graner, A., and E. Bauer. 1993. RFLP mapping of the ym4 virus resistance gene in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86:689-693.
Hvid, S., and G. Nielsen. 1977. Esterase isozyrne variants in barley. Hereditas 87: 155-162.
Kaiser, R., and W. Friedt. 1989. Chromosomal location of resistance to barley yellow mosaic virus in German winter barley identified by trisomic analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 77: 241-245.
Kaiser, R., and W. Friedt. 1992. Gene for resistance to barley mild mosaic virus in German winter barley located on chromosome 3L. Plant Breeding 108: 169-172.
Kawada, N. 1991. Resistance genes to barley yellow mosaic virus. In: MUNK L. [Ed.], Proc. VIth Int. Barley Genet. Symp., Helsingborg, Sweden. Barley Genetics VI, 616-618.
Konishi, T., N. Kawada, H. Yoshida, and K. Soutome. 1989. Linkage relationships between two loci for the barley yellow mosaic resistance of Mokusekko 3 and esterase isozymes in barley (Hordeum vulgare, L.). Japan J. Breed. 39: 423-430.
Nielsen, G., and H.B. Johansen. 1986. Proposal for the identification of barley varieties based on the genotypes for 2 hordein and 39 isozyme loci of 47 reference varieties. Euphytica 35: 717-728.
Ordon, F., and W. Friedt. 1993. Mode of inheritance and genetic diversity of BaMMV resistance of exotic barley germplasms carrying genes different from 'ym4'. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86:229-233.
Wagner, H., W.E. Weber, and G. Wricke. 1992. Estimating linkage relationships of isozyme markers and morphological markers in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) including families with distorted segregations. Plant Breeding 108: 89-96.