

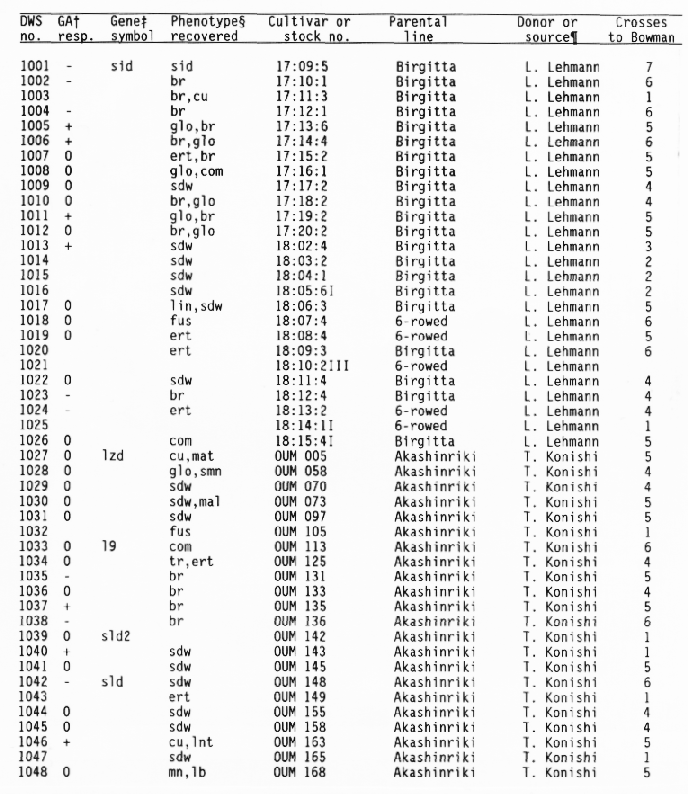
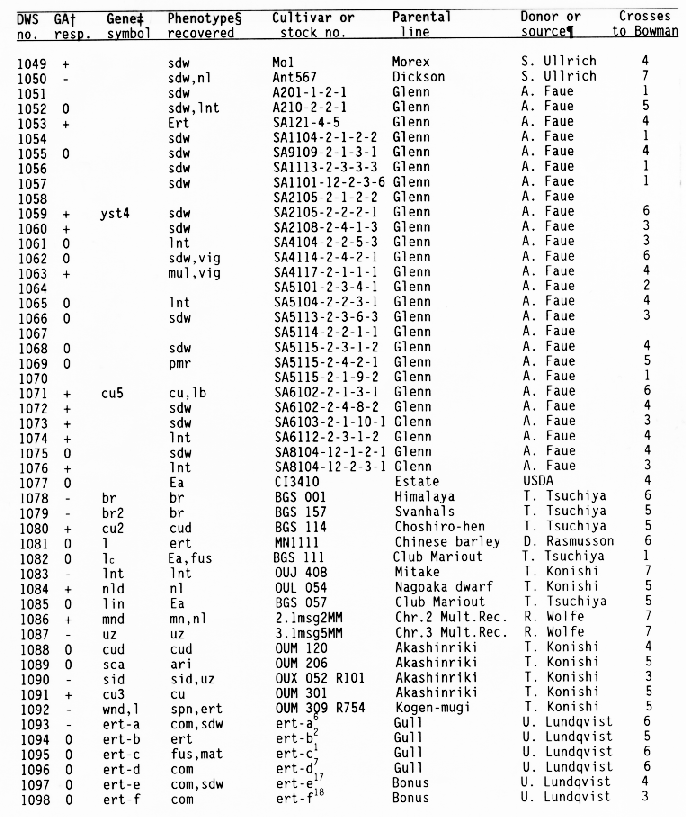
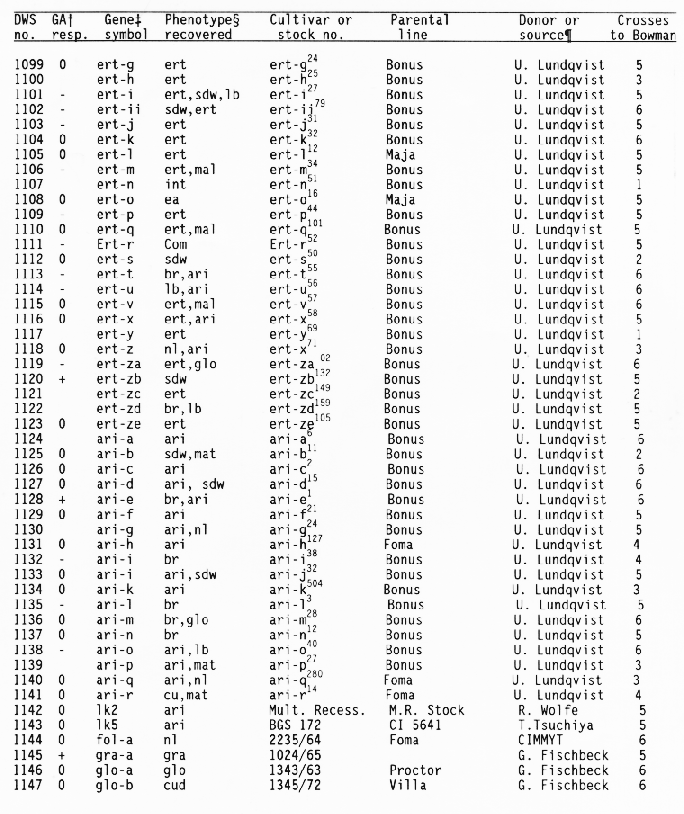
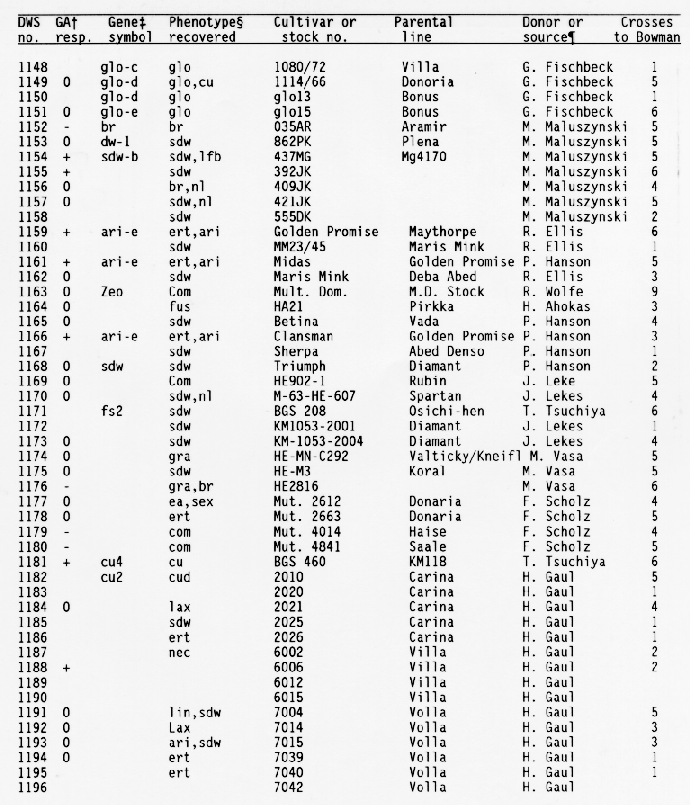
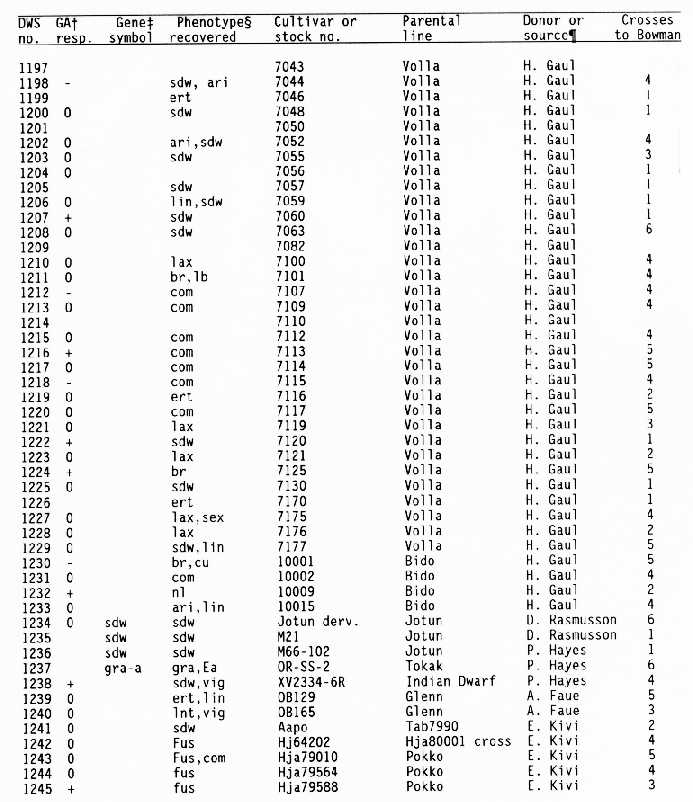
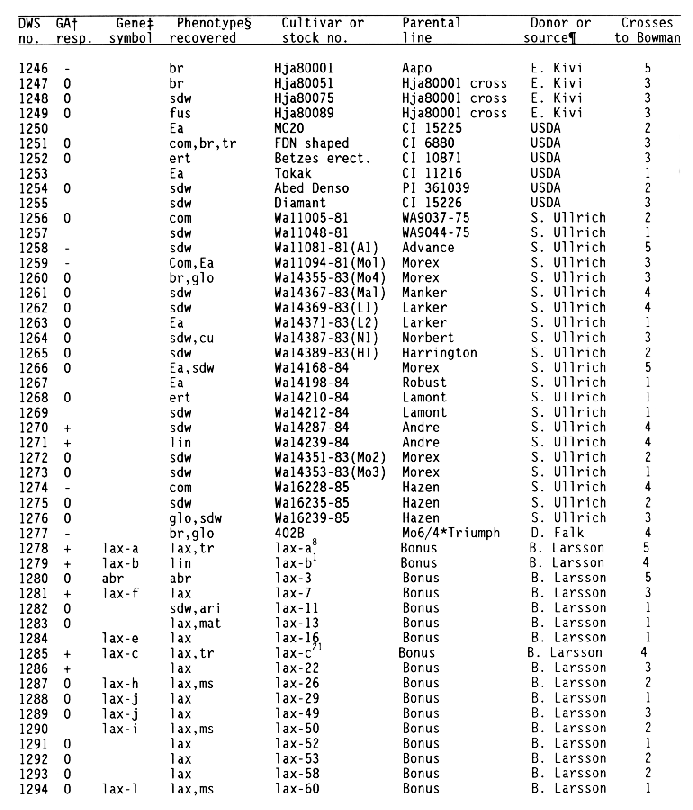
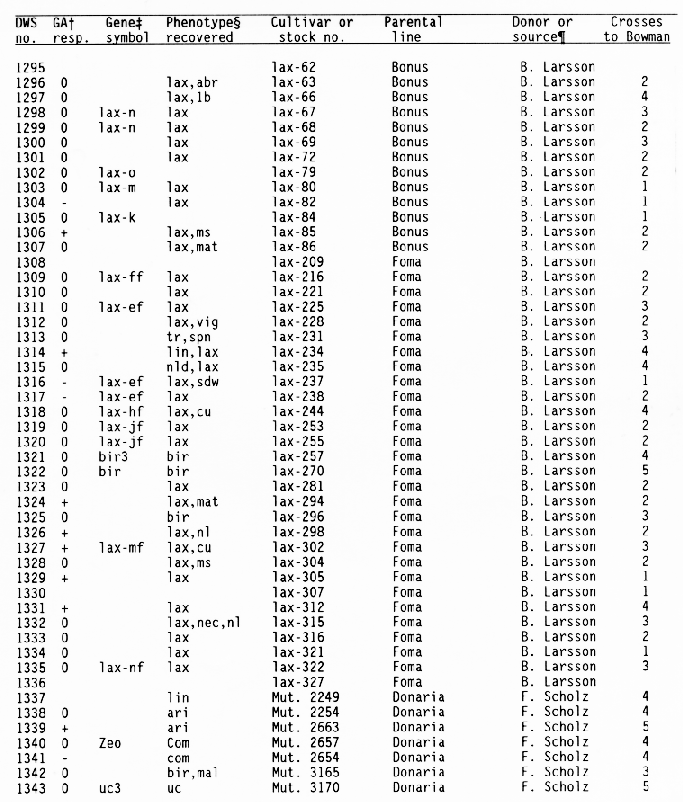
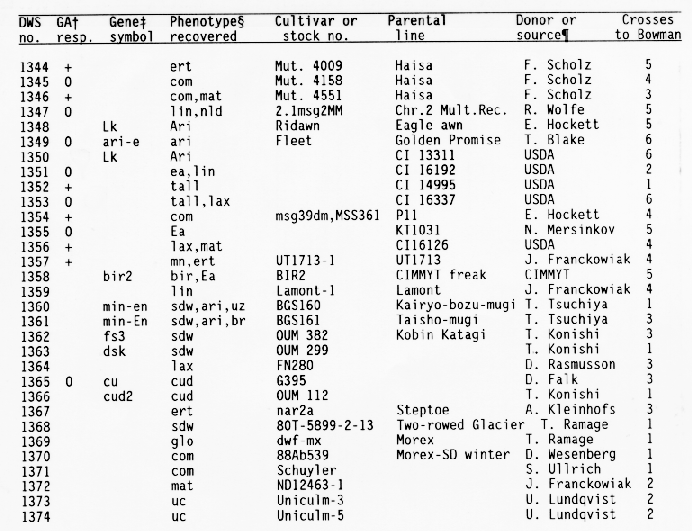
+ Response
of the subcrown internode to application of gibberellic and during
germination:
- = GA insensitive with no or little elongation,
0 = GA sensitive with increased elongation,
+ = GA constitutive
with similar elongation in treated and untreated seedlings, and
blank = not tested.
+
+ Gene symbols have been
described in the Barley Genetics Newsletter and by Sogaard and
Wettstein-Knowles (1987).
Codes used for phenotypic traits were: abr = long basal rachis internode, ari = reduced awn length, bir = branched spike, br = brachytic growth habit, com = compact spike with short rachis internodes, cu = curly leaves, cud = curly leaves and short culms, ea = early maturity, ert = semicompact spike, fus = fusiform or pyramid-shaped spike, glo = altered seed shape, gra = semidwarf with premature spike emergence, lax = long rachis internodes, lb = long basal rachis internode, lin = low number of rachis internodes, lfb = leafy basal rachis node, lnt = reduced tillering, mal = malformed spike, mat = delayed heading, mn = many elongated internodes, nec = leaf necrosis or necrotic spot, ms = partial sterility, nl = narrow leaf, ped = shortened peduncle, pmr = premature ripening, sdw = semidwarf or reduced plant height, sex = shrunken endosperm, sid = single elongated internode, smn = semicovered caryopsis, spn = spiral or curved upper peduncle, vig = much reduced vigor, tr = triple or broad awn, and uc = little or no tillering.
List of individuals and institutions who have contributed
entries to the semidwarf barley collection: H. Ahokas, Univ. of
Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland; T. K. Blake, Montana State Univ.,
Bozeman, MT, USA; H. Bockelman, USDA/ARS, National Small Grains
Collection, Aberdeen, ID, USA; R. P. Ellis, Scottish Crop
Research Institute, Dundee, Scotland, UK; D. E. Falk, Univ. of
Guelph, Guelph, Ontario, Canada; A. Faue, North Dakota State Univ.,
Fargo, ND, USA; G. Fischbeck, Lehrstuhl fur Planzenbau und Planzenzuchtung,
FreisingWeihenstephan, Germany; H. P. K. Gaul, Biologische
Bundesanstalt fur Land-und Forstwirtschaft, Grunbach, Germany;
P. R. Hanson, Plant Breeding Institute, Cambridge, England;
E. A. Hockett, Montana State Univ., Bozeman, MT, USA; P. M.
Hayes, Oregon State Univ., Corvallis, OR, USA; E. I. Kivi, Hankkija
Plant Breeding Institute, Hyryla, Finland; A. Kleinhofs, Washington
State Univ., Pullman, WA, USA; T. Konishi, Okayama Univ., Kuraschiki,
Japan; H. E. B. Larsson, Agricultural Univ. of Sweden, Uppsala,
Sweden; L. Lehmann, Svalov, Sweden; J. Lekes, Cereal Research
and Breeding Institute, Kromeriz, Czechoslovakia; U. Lundqvist,
Svalov, Sweden; M. Maluszynski, Plant Breeding and Genetics Section,
Joint FAO/IAEA Division, Vienna, Austria; N. Mersinkov, The Institute
of Barley, Karnobat, Bulgaria; R. T. Ramage, USDA/ARS, Univ. of
Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA; D. C. Rasmusson, Univ. of Minnesota,
St. Paul, MN, USA; F. Scholz, Zentralinstitut fur Genetik und
Kulturpflanzenforschung, Gatersleben, Germany; T. Tsuchiya, Barley
Genetic Stock Center and Colorado State Univ., Fort Collins,
CO, USA; S. E. Ullrich, Washington State Univ., Pullman, WA, USA;
M. Vasa, Oseva, Slechtitelske a Semenarske Podniky, Praha, U Toriren,
Czechoslavakia; D. M. Wesenberg, USDA/ARS, National Small Grains
Collection, Aberdeen, ID, USA; and R. I. Wolfe, Agriculture
Canada, Beaverlodge, Alberta, Canada.