

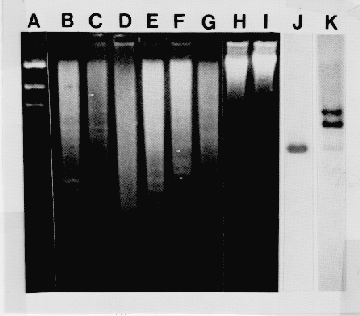
A simple method of DNA extraction from plants which shows good resolution for single or multiple copy autoradiographic bands upon genomic blot analysis (Fig. 1) is described. This procedure obviates the need for 1) time consuming and expensive CsCl density gradient steps, 2) lengthy proteinase K digestions or dialysis, and 3) the use of large quantities of corrosive phenol. We have consistently obtained high yields (Table 1) and high MW DNA (> 50 kb) with quick processing times. One of the problems often encountered when extracting plant DNA is polysaacharide contamination which inhibits most DNA modifying enzymes. The method presented here eliminates these polysaacharides by CTAB (hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide) precipitation (Murray and Thompson, 1980; Rogers and Bendich, 1988).
Young leaves were ground to a powder in liquid nitrogen in a mortar and pestel with a little washed sea sand (Fischer). To the transferred powder in centrifuge tubes, one volume of hot (65°C) CTAB buffer (2% CTAB w/v, 20 mM EDTA, 1.4M NaCl, 1% PVP, 100 mM Tris, pH8.0) was added. The mixture was placed at 65{o}C for 5 min; then one volume of chloroform/ isoamyl alcohol (24:1) added and mixed. After centrifugation (500 × 9, 10 min), 1/5 volume of a 5% CTAB solution (5% CTAB, 0.7M NaCl) was added to the supernatant and mixed. The chloroform/isoamyl alcohol step and centrifugation was repeated and DNA precipitated from the supernatant with 2 volumes of 95% ethanol. Following centrifugation, the DNA pellet was dried and resuspended in TE (lOmM Tris, lmM EDTA, pH 8.0). If residual nucleases are a problem (as shown by DNA degradation on EtBr stained agarose gels), the DNA can be treated with proteinase K (40 ug/ml, 1 hr, 50°C). RNase treatment is unncessary when transferring restricted DNA fragments fragments to charged nylon membranes (Zeta Probe) by the alkaline blotting procedure (Reed, 1986).
Electrophoretic and genomic blot analysis of restricted DNA fragments of DNA extracted from various plants as described. Lands A-I: Ban Hl restricted DNA run on 0.8% agarose gel from 250 volt-hrs and stained with EtBr.
Acknowledgments
This work has been funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the Ontario Ministry of Agriculture and Food.
References:
McIntyre, C.L., S. Pereira, L.B. Moran, and R. Appels. 1990. Genome 33:635-640.
Murray, M.G., and W.F. Thompson. 1980. Nucleic Acids Res. 8:4321-4325.
Reed, K.C. 1986. Bio-Rad Bulletin 1233:1-5.
Rogers, S.O., and A.J. Bendich. 1988. Plant Mol. Bio. Manual A6:1-10.