

The Hor4 (HrdG) locus is located proximally to Hor1 on the short arm of barley chromosome 5, and has only been demonstrated in 'Elinga', and derived lines (Netsvetaev and Sozinov, 1984; Shewry et al., 1987; 1988). Although Hor4 is close to Hor1, the encoded protein appears to be most closely related to the B hordeins encoded by Hor2. This suggests that Hor4 originated from translocation of part of the Hor2 locus, possibly in an ancestor of Elqina (Shewry et al., 1988).
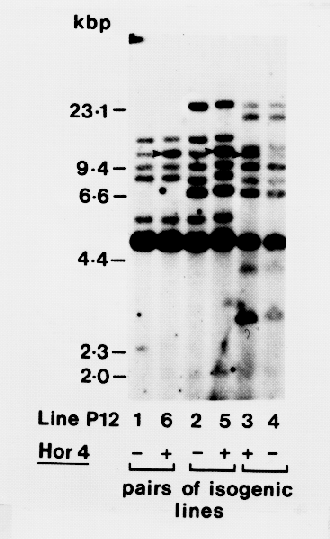
We have prepared genomic DNA from three pairs of lines which are isogenic for Horl and Hor2, but differ in the absence or presence of the Hor4 gene product. The DNA was then digested with the restriction endonuclease Hind III and the fragment separated by electrophoresis, transferred to a nylon membrane and probed with a 32P-labelled cNDA related to B hordein (pB 11) (Forde et al., 1985). An additional hybridizing band, which presumably corresponded to the Hor4 gene, was present in P12/3 (Hor4+) compared with P12/44 (Hor4-). Bands with similar mobilities were also present in the other two Hor4+ lines (P12/5 and P12/6), although in both cases they co-migrated with weakly hybridizing bands which were also present in the isogenic Hor4- lines (P12/2 and P12/1, respectively).
The intensity of hybridization suggests that Hor4 consists of only one or two genes, while the cross-hybridization with the B hordein related probe confirms that the Hor4 gene product is closely related to B hordein.
Acknowledgment:
We are grateful to Dr. V. P. Netsvetaev (N.I. Vavilov Institute of General Genetics, Moscow) for supplying seeds of P12/1 to P12/6.
References:
Forde, J. G., M. Kreis, M. S. Williamson, R. J. Fry, J. Pywell, P. R. Shewry, N. Bunce, and B. J, Miflin. 1985. Short tandem repeats shared by B- and C-hordein cDNAs suggest a common evolutionary origin for two groups of cereal storage protein genes. EMBO. J. 4:9-15.
Netsvetaev, V. P., and A. A. Sozinov. 1984. Location of a hordein G locus (Hrd G) on chromosome 5 of barley. BGN 14:4-6.
Shewry, P. R., S. Parmar, R. White, and J. Franklin. 1987. Mapping and biochemical analysis of the Hor4 (Hrd G) locus encoding B hordein-like polypeptides. BGN 17:87-89.
Shewry, P. R., S. Parmar, J. Franklin, and R. White. 1988. Mapping and biochemical analysis of the Hor4 (Hrd G), a second locus encoding B hordein seed proteins in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Genet. Res. Camb. 51:5-12.