

Eleven mutants for globe shaped grains were included in this study. Most of the mutants originated from x-ray seed treatment of cultivars Donaria, Proctor, and Villa.
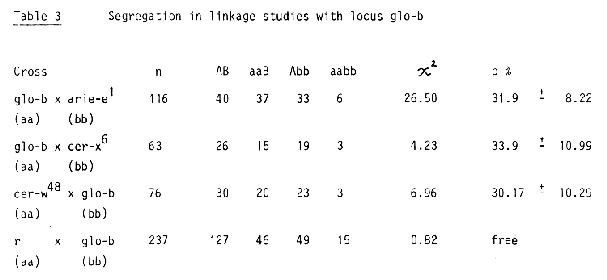
The translocation lines developed by Hagberg and Hagberg (1968) were used to determine chromosomes carrying the mutant loci. Marker genes r arie-e1, cer-x6 and cer-w48 for chromosome 7 were used to determine linkage relationships.
The x2 test was applied to determine critical segregations. Recombination frequencies were estimated by the maximum likelihood- method (Mather, 1951; Allard, 1956).
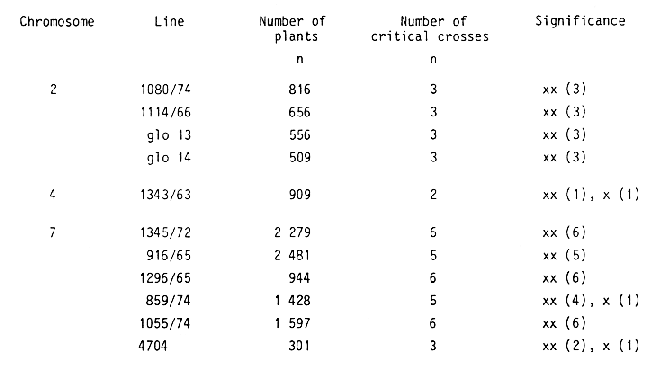
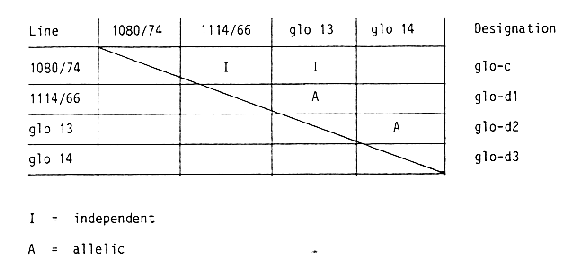
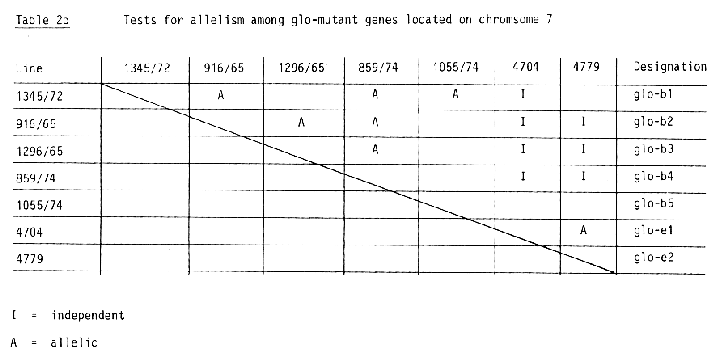
Five mutant loci designated glo-a, glo-bl, glo-b2, glo-c and glo-d have been located earlier on chromosomes 4 (glo-a), 7 (glo- b) and 2 (glo-c and glo-d) (Fischbeck and Hauser, 1976). Sodkiewicz and Gorney (1982) reported about two recessive mutants obtained from cultivar "Damazy". Table 1 summarizes critical segregations obtained from crosses of the 11 mutants included in this study with translocation lines. The results of tests for allelism for mutant loci assigned to chromosomes 2 and 7 are summarized in Table 2a and 2b respectively. It is concluded that chromosome 2 carries two loci for globe shaped grains which are independently inherited. Three mutants (1114/66; glo 13 and glo 14) are either allelic or closely linked. In accordance with designation which have been used earlier, it is suggested to assign the gene symbols glo-dl, glo-d2, and glo-d3 to these mutant lines and the gene symbol glo-c to the other locus on chromosome 2 represented by mutant line 1080/72. Tests for allelism for the 6 mutant lines assigned to chromosome 7 (Table 1) and 1 additional line (4979) mentioned in Table 2b revealed again the presence of two independently inherited loci. While the results with mutant lines 1345/72 and 916/65 confirmed earlier results of allelism or close linkage for which the designation glo-bl and glo-b2 has been respectively. Furthermore mutant lines 1296/65, 859/74 and 1055/74 showed allelism or close linkage to the same locus and consequently are designated glo-b3, glo-b4 and glo-b5 respectively. The mutant lines 4704 and 4979 showed allelism or close linkage to each other but independent inheritance in all tests with mutant lines from locus glo-b. They clearly represent a new locus for globe shaped grains on chromosome 7. It is suggested to assign the designation glo-el and glo-e2 to these lines respectivly. The association of locus glo-a designated earlier to mutant line 1.343/63 with chromosome 4 has been confirmed (Table 1).
Literature
Allard, R. W., 1956. calculation of Hilgardia Vol. 24 Formulas and tables to facilitate the recombination values in heredity. (No. 10) 235-278.
Hauser, J., und G. Fischbeck. 1976. Unterschungen zur Lokalisie- rung einiger Mutationen von Gerste (Hordeum sativum) . Z. Pflanzenzüchtung, 77, 269-280.
Hagberg, A. and G. Hagberg. 1968. Mutations in plant breeding. II IAEA, Vienna 129-137.
Mather, K. 1951. The measurement of linkage in heredity. 2nd edn. Melhuen & Co. LTD, Longon. 149 p.
Sodkiewicz and A. G. Gorney. 1982. Barley mutants with long- shaped and globe-shaped grains. BGN, 12, 4-7.
Sogaad, B. 1971. The Localization of Eceriferum Mutants in Barley, Ph.D. Thesis University of Copenhagen and Agricultural Research Department Atomic Energy Commission, Reearch Establishment Risø, Denmark.