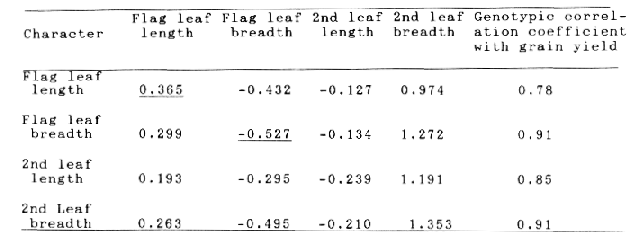
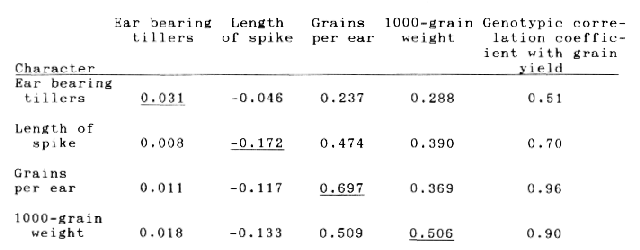
Two hulled barley cultivars namely, DL36 and Jyoti and their nine induced macro-mutants were studied for path coefficient analysis using genotypic correlation coefficients. Analysis was done in two sets. The first set consisted of four leaf characters viz. length and breadth of flag leaf and length and breadth of second leaf as casual characters and grain yield as the effect. The second set consisted of four yield components viz. ear bearing tillers, length of spike, grains per ear and 1000 grain weight as independent characters and grain yield as dependent character.
There was positive genotypic correlation of grain yield with all the characters. Among the leaf characters, second leaf breadth had the highest positive direct effect (1.353) on grain yield (Table 1). Flag leaf length had also positive direct effect. Flag leaf breadth and second leaf length had negative direct effects which were overcome by the positive indirect effects via other characters. Among the yield components, grains per ear had the highest positive direct effect (0.697) followed by 1000-grain weight (0.506) and ear bearing tillers (Table 2). Direct and indirect effects of length of spike were negative . The results indicated that grain boldness grains per ear, length of flag leaf and breadth of second leaf are important characters to be considered for selection and improvement of barley.